事务
事务是数据库操作最基本单元,逻辑上一组操作,要么都成功,如果有一个失败所有操 作都失败
典型场景:银行转账 张三 转账 100 元 给 李四; 张三少 100,李四多 100
事务四个特性(ACID)参考文章
- 原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性
事务操作(搭建事务操作环境)
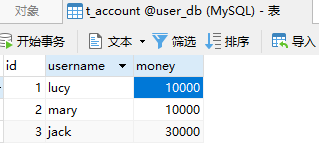
创建 service ,搭建 dao,完成对象创建和注入关系。
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
public class AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
}在 dao 创建两个方法:多钱和少钱的方法, 在 service 创建方法(转账的方法)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
// 多钱
public void addMony(Integer money, String name) {
String sql = "update t_account set money = money + ? where username = ?";
Object[] args = {money, name};
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
System.out.println(update);
}
// 少钱
public void reduceMoney(Integer money, String name) {
String sql = "update t_account set money = money - ? where username = ?";
Object[] args = {money, name};
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
System.out.println(update);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 转账的方法
public void accountMoney(){
// lucy 少100
accountDao.reduceMoney(100, "lucy");
// mary 加100
accountDao.addMony(100, "mary");
}
}
上面的代码正常执行没有问题,但是如果代码执行过程中出现异常,有问题,可能会出现 lucy 少了100 但是 mary没有加100。
解决步骤:
1 | // 转账的方法 |
事务操作
- 事务添加到 JavaEE 三层结构里面 Service 层(业务逻辑层)
- 在 Spring 进行事务管理操作 ;两种方式:编程式事务管理、声明式事务管理(推荐使用)
- 声明式事务管理
- 基于注解方式(推荐使用)
- 基于 xml 配置文件方式
- 在 Spring 进行声明式事务管理, 底层使用 AOP 原理
- Spring 事务管理 API :提供一个接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对不同的框架提供不同的实现类
注解声明式事务管理⭐
在spring配置文件配置事务管理器。
1
2
3
4<!-- 创建事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref = "dataSource"></property>
</bean>在 spring 配置文件中引入名称空间
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx",开启事务注解1
2<!-- 开启事务注解 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>在 service 类上(或者色如此vice类里面方法上)添加事务注解。
@Transactional添加在类上面,则表示这个类上的所有方法都添加了事务。@Transactional添加在类里的方法上,则表示为这个方法添加事务。
1
2
3
// 事务注解
public class AccountService {
以上就完成了基于注解声明式事务管理。
声明式事务管理的参数配置
propagation 事务传播行为
多事务方法直接进行调用,这个过程中事务 是如何进行管理的
1 | // 事务1 |
spring框架事务传播行为有七种:下面只介绍常用的两种传播行为
REQUIRED:如果有事务在运行,当前的方法就是在这个事务内运行,否则就会启动一个新的事务,并在自己的事务内运行。REQUIRED_NEW:当前的方法必须启动新事务,并在它自己的事务内运行,如果有事务正在运行,应该将他挂起。SUPPORT:如果有事务在运行,当前的方法就在这个事务内运行,否则它可以不运行在事务中。
ioslation 事务隔离级别
事务有特性称为隔离性,多事务操作之间不会产生影响。不考虑隔离性产生很多问题。
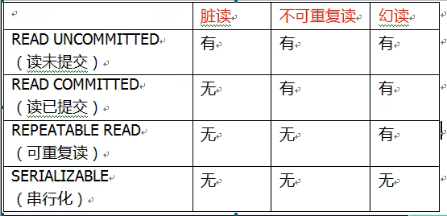
有三个读问题:脏读、不可重复读、虚(幻)读。 参考文章
- 脏读: 一个未提交事务读取到另一个未提交事务的数据。
- 不可重复读: 一个未提交事务读取到另一提交事务中修改的数据。
- 虚读: 一个未提交事务读取到另一提交事务添加数据。
解决:通过设置事务隔离级别,解决三个读问题
1 |
事务的隔离级别:(和MySQL数据库中的隔离级别完全对应,在MySQL中默认是REPEATABLE_READ)
timeOut超时时间
- 事务需要在一定时间内进行提交,如果不提交进行回滚
- 默认值是 -1(不超时),设置时间以秒单位进行计算。
readOnly 是否只读(查询)
- 读:查询操作,写:添加修改删除操作
- readOnly 默认值 false,表示可以查询,可以添加修改删除操作
- 设置 readOnly 值是 true,设置成 true 之后,只能查询
rollbackFor回滚
设置出现哪些异常进行事务回滚
noRollbackFor不回滚
设置出现哪些异常不进行事务回滚
XML声明式事务管理
在 spring 配置文件中进行配置 :
第一步 配置事务管理器
1
2
3
4
5<!-- 创建事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 注入数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref = "dataSource"></property>
</bean>第二步 配置通知
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9<!-- 2.配置通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txadvice">
<!-- 配置事务参数 -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 指定哪种规则的方法上面添加事务 -->
<tx:method name="accountMoney" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ"/> <!-- 表示在accountMoney方法上面添加事务 -->
<!--<tx:method name="account*"/>--> <!-- 这种写法也可以 -->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>第三步 配置切入点和切面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7<!-- 3.配置切入点和切面,需要引入名称空间aop -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.xzt.springaffair.service.AccountService.*(..))"/>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pt"></aop:advisor> <!-- 将txadvice的事务作用与pt方法上 -->
</aop:config>
完整配置文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
<!-- 引入context名称空间 -->
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 开启组件扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xzt.springaffair"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 引入外部属性文件配置连接池 -->
<!--引入外部属性文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置连接池-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${prop.userName}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建JdbcTemplate对象 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源信息,使用set方法注入 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref = "dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务注解,使用注解进行事务管理 -->
<!-- <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven> -->
<!-- 2.配置通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txadvice">
<!-- 配置事务参数 -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 指定哪种规则的方法上面添加事务 -->
<tx:method name="accountMoney" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ"/> <!-- 表示在accountMoney方法上面添加事务 -->
<!--<tx:method name="account*"/>-->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 3.配置切入点和切面 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.xzt.springaffair.service.AccountService.*(..))"/>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pt"></aop:advisor> <!-- 将txadvice的事务作用与pt方法上 -->
</aop:config>
</beans>完全注解声明式事务管理⭐
创建配置类
config.java1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55package com.xzt.springaffair.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @author xzt
* @version 1.0
*/
// 配置类
// 开启组件扫描
// 生成AspectJ 代理对象 AOP
// 开启事务
public class Config {
// 创建数据库连接池
public DruidDataSource getDruidDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_db");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
// 创建JdbcTemplate模板对象
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
// 到IOC容器中,根据类型找到dataSource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
// 注入DataSource
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
// 创建事务管理器对象
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
public void testDemo() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
AccountService accountService = context.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class); // 根据配置文件获取context
accountService.accountMoney();
}